
Here's how to ease constipation
Causes of constipation
There are many causes of constipation, including diet, medications, activity, diseases and disorders. Children can also suffer from intentional stool retention, which is constipation due to stress when they’re not ready for toilet training.

Insufficient water and fibre – A diet that includes an excessive intake of soft drinks, with insufficient drinking water, fruits, and vegetables

Taking some medication – Antipyretics, analgesics, cough medicine, diarrhoea medicine could be a cause of dry stools and difficult bowel movements

Anal fissure – Difficult and painful bowel movements

Emotional disorders – Being in a stressful home or family atmosphere, with divorced parents, a new baby, etc.

Diseases – Development of disorders related to the colon, rectum, nervous system, blood, etc.

Inactivity – That causes inactive peristalsis
Intentional stool retention
Some children under the age of 5 cannot control their faecal excretion reflux, or have a fear of sitting on the toilet which could cause difficult bowel movements. As such, they choose to intentionally hold back their stool, a habit that can cause constipation.

Your child refuses to go to the toilet
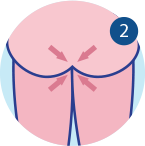
This causes anal muscle spasms and squeezed buttock muscles
As a result, faeces is pushed up to the rectum valve
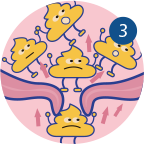
In turn, this causes constipation in your child
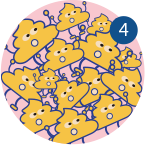
Leading to colon dilation and decreased rectal sensitivity

This results in prolonged faecal cumulation, contributing to constipation
Symptoms
Constipation is generally difficult to define, as there are no clear indications of what is ‘normal’ in terms of the frequency of bowel movements, and symptoms may vary from child to child. Here are some signs if you’re concerned that your child could be suffering from constipation.

Difficult and infrequent bowel movements

Refusal to go to the toilet

Underwear is sometimes unknowingly soiled

Experiences anal pain, has uncontrolled bowel movements or blood in stool

Stool looks solid, lumpy, or generally abnormal

Child has abdominal pain and a poor appetite

Infant passes meconium after 48 hours or more at birth
Home fixes
Not all constipation incidents need medical attention. Before you rush to your medical practitioner, you may want to try these tips at home to ease the situation.

TUMMY RUB
Massage your child’s tummy with warm hands using gentle pressure

MORE FRUITS
Apples, pears and prunes are great for making bowel movements smoother

HYDRATE OFTEN
Make sure your child is drinking enough water throughout the day

HIGHER FIBRE
Bran flakes, oatmeal, brown rice, and beans can help to soften stools

WARM BATH
This can help to relax the anal muscles and help to pass the stool

RIGHT POSITION
Use a footstool to ensure that the feet are properly supported
The Bristol stool scale
The Bristol stool scale is a good indication of whether or not your child is suffering from constipation, as normal faeces should be the texture of Types 4 to 6, rather than dry, lumpy pieces in Types 1 to 3.
Physical constipation
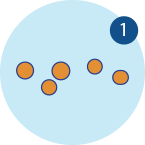
In hard lumps or shaped like nuts
Functional constipation
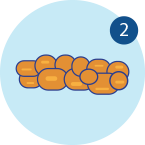
Sausage-shaped or lumpy stools
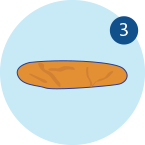
Like a sausage but with many cracks on the surface
Normal bowel movements
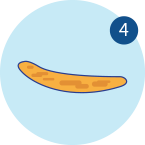
Like a sausage or snake, smooth & soft
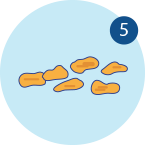
Soft blobs with clear cut edges
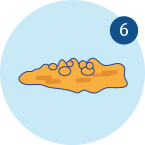
Fluffy pieces with ragged edges or mushy stools
Diarrhoea
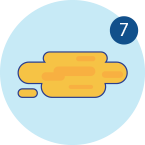
Watery with no solid pieces or entirely liquid
Effects of prolonged constipation
If your child has experienced this condition for a prolonged period, it would be wise to call your doctor. Do seek medical attention especially if your child is suffering from any of these symptoms.
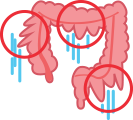
Colon dilation (where the colon is unnaturally extended)
Rectocele (or rectum prolapse)

Poor appetite of your child

Slow weight gain in your child

Persistent abdominal pain

Vomiting
RELATED ARTICLES
